what is a subchondral cyst
 Surgical Treatment of Subchondral Bone Cysts of the Acetabulum With Calcium Phosphate Bone Substitute Material in Patients Without Advanced Arthritic Hips - ScienceDirect
Surgical Treatment of Subchondral Bone Cysts of the Acetabulum With Calcium Phosphate Bone Substitute Material in Patients Without Advanced Arthritic Hips - ScienceDirectWhat about subcondral bone cyst? Subcondral bone cysts are liquid bags that form within a person's joints. Cysts occur in the subcondral bone, the bone layer just below the cartilage. The subcondral bone acts as a damper in the joints that support weight, such as knees, hips and shoulders. The fluid inside the subcondral bone (SBCs) is hyaluronic acid, a component found in synovial fluid, which is the thick substance that lubricates the joints, allowing the bones to slide between themselves without friction. Risk factors for SBCs include and smoke, but the exact cause is unknown. Symptoms include joint pain and discomfort. Lifestyle changes help relieve symptoms and can prevent the formation of other CBCs. Quick data on SBCs: Some experts believe that SBCs are a precursor of osteoarthritis (OA), which itself is a painful condition that affects more than adults in the United States. OA causes cartilage and bones within a joint to decompose gradually. SBCs are considered one of the four cardinal radiological findings or key to OA. However, in one of the 806 people with OA on the knee, the SBCs found in only 30.6 percent of them. Other conditions besides OA, such as, also cause cysts to form in the bone joints. Although the cause is unknown, it is believed that the SBCs are the result of repeated bone. This stress is caused by increased blood flow pressure faster to the subcondral bone, something seen in people with AO. Certain features and behaviors can increase the risk of developing a CBS. These include: It is recommended that SBCs be not treated directly. Because of the risk of infection, these cysts should not be eliminated. However, they can go back on their own. As a result, treatment usually involves making lifestyle changes and providing symptom relief. Some people may benefit from replacing the joint if the problems are continuous or progressive. Treatments for SBCs are as follows: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)These free-selling analgesics, such as ibuprofen and , can reduce symptoms of SBCs. It is always advisable to consult with a doctor before taking . Long-term use should be avoided. Low-impact activities It is recommended to choose low-impact activities such as swimming, aerobic and cycling. These put less pressure on the knees and hip joints than high-impact activities, such as running and jumping, which can exacerbate OS and SBC symptoms and cause new joint damage over time. Weight Management Keeping a healthy weight reduces excess stress in the joints and can reduce the rate of cartilage loss. Quit Smoking As this is a risk factor for the development of osteoarthritis, and avoiding second-hand smoke can reduce symptoms of SBCs and OAs. Ultrasound Therapy At least one suggests that the delivery of ultrasonic therapy located to cartilage and subcondral bone can help treat the OA. However, much more research is needed in this area. Physiotherapy According to mild degenerative disease, of which SBCs can be a feature, it can be treated with . If you are present, the symptoms of SBCs may include: There are only some symptoms associated with SBCs, as they are usually considered an OA symptom, particularly progressive OA. SBCs are considered an OA symptom or other joint conditions. They can resolve for themselves or persist in the long term. SBCs can cause pain and contribute to disease progression. The best way to treat these cysts is to manage OA symptoms and other joint conditions. Last medical review on August 17, 2017Most recent newsRelated coverage
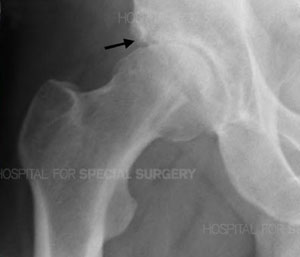
Hip Cysts | Subchondral Bone Cysts | HSS #1 for Orthopedics
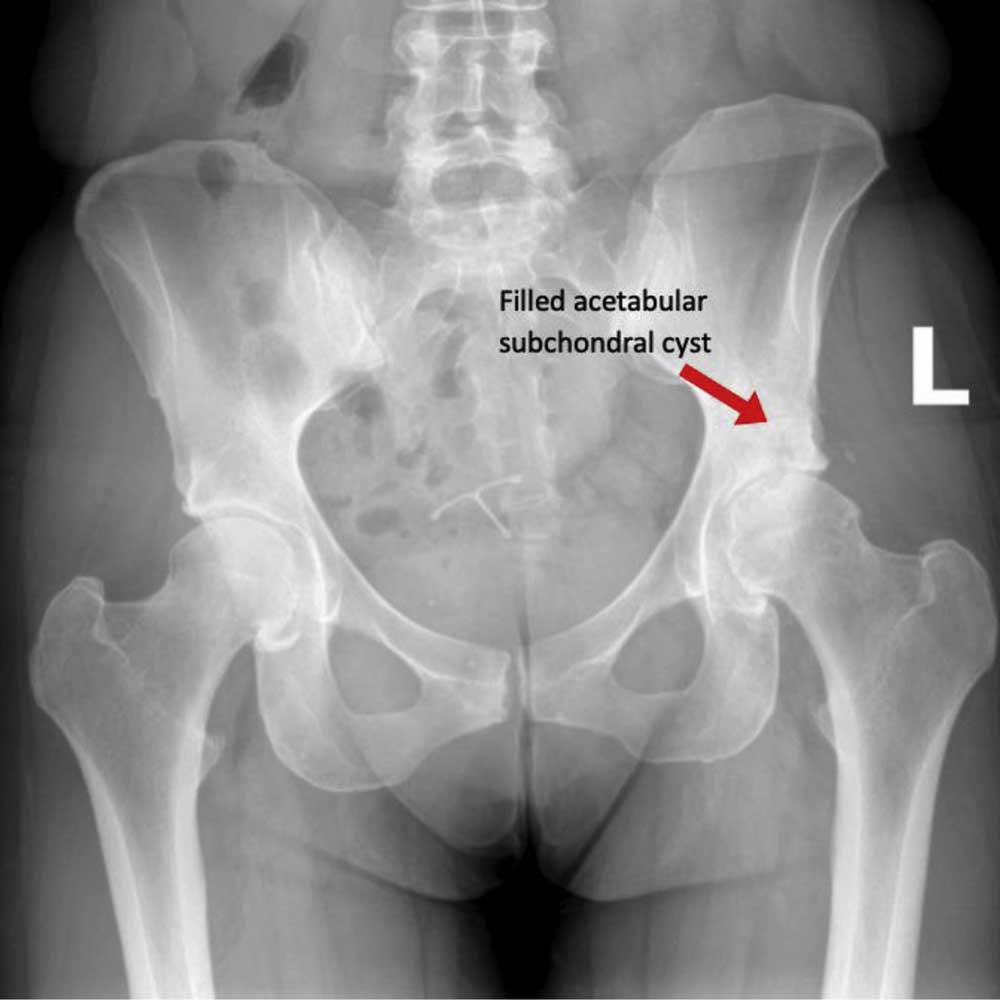
Hip Cysts | Acetabular Paralabral Cyst & Subchondral Cyst | FAI | Manhattan, New York City, NY

Degenerative subchondral bone cyst | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org
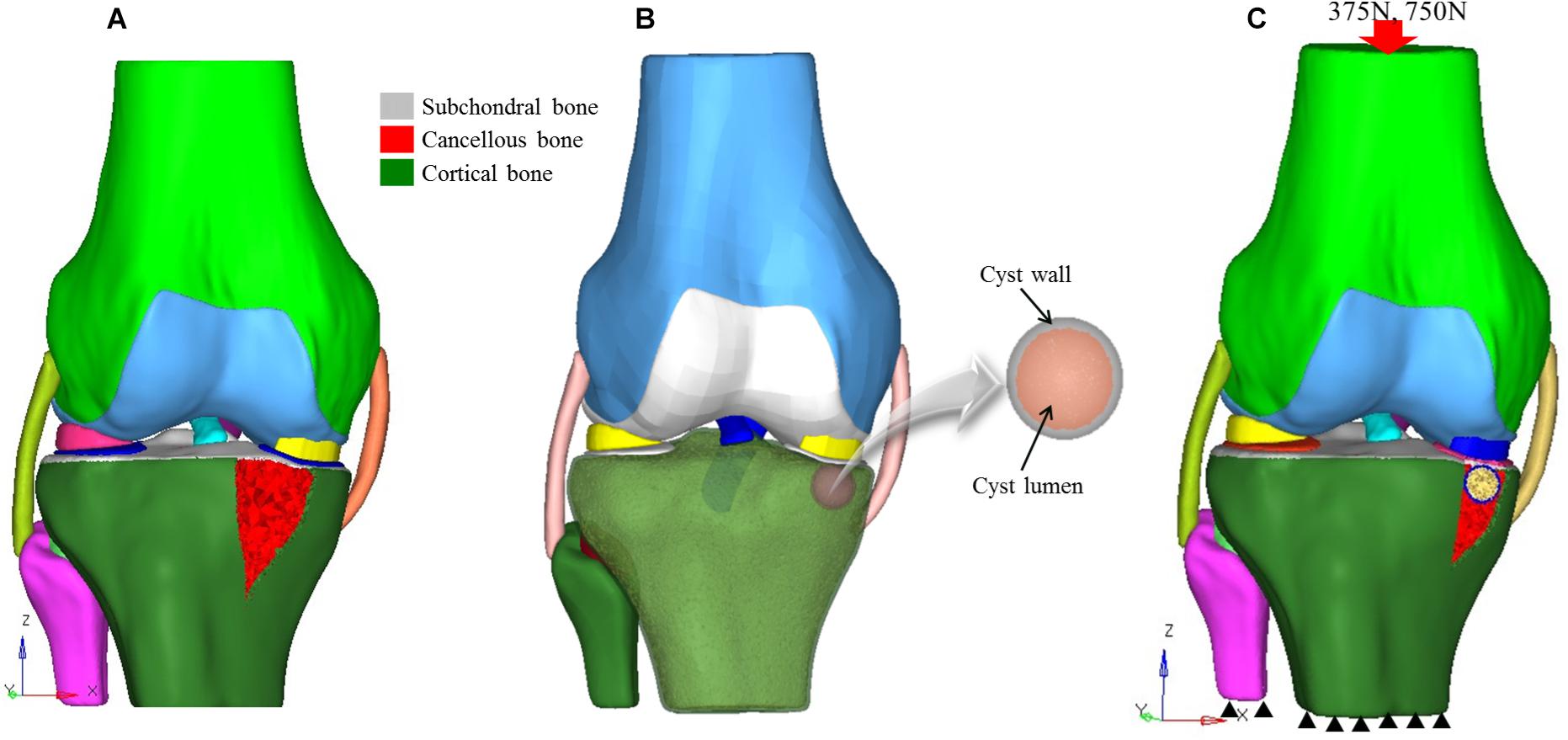
Frontiers | Multiple Subchondral Bone Cysts Cause Deterioration of Articular Cartilage in Medial OA of Knee: A 3D Simulation Study | Bioengineering and Biotechnology

Facts about subchondral bone cyst | Usapang Pangkalusugan - YouTube

Subchondral cyst in a hemophilic knee: (a) Anteroposterior radiograph... | Download Scientific Diagram

Subchondral cyst (geode) of the femoral head | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org

Subchondral Bone Cyst: Case 24 | SpringerLink

Subchondral Bone Cysts in Horses | Kimberly's Korner
Subchondral Bone Cyst – Oklahoma Farm & Ranch

Detection of Osteophytes and Subchondral Cysts in the Knee with Use of Tomosynthesis | Radiology
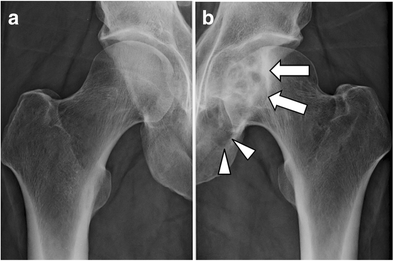
Uncommon observation of bifocal giant subchondral cysts in the hip: diagnostic role of CT arthrography and MRI, with pathological correlation | SpringerLink

MRI-detected subchondral bone marrow signal alterations of the knee joint: terminology, imaging appearance, relevance and radiological differential diagnosis - ScienceDirect
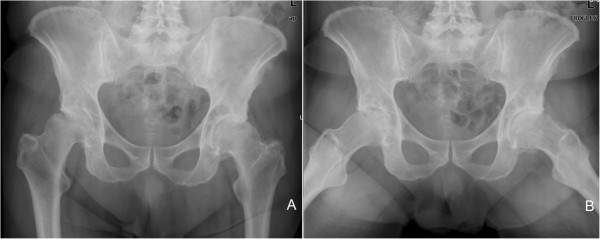
An atypically located large subchondral cyst in an osteoarthritic hip joint: a case report | Journal of Medical Case Reports | Full Text

PA view of right wrist reveals a subchondral cyst in the distal radius... | Download Scientific Diagram
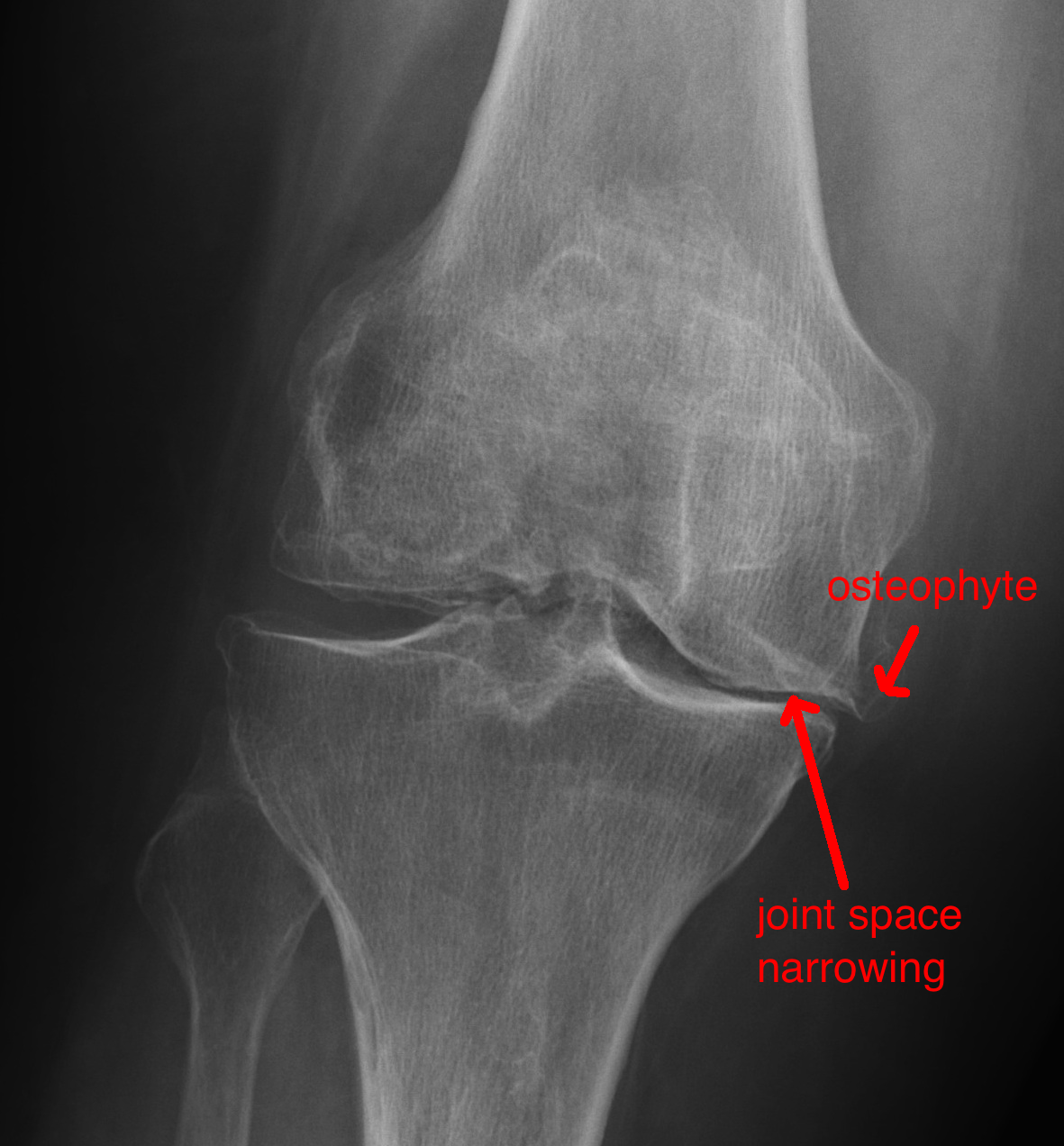
Leg/Knee Case 10 Diagnosis: Department Test: Feinberg School of Medicine: Northwestern University
Musculoskeletal "don't touch" lesions: pictorial essay

The impact of subchondral bone cysts on local bone stresses in the medial femoral condyle of the equine stifle joint - ScienceDirect
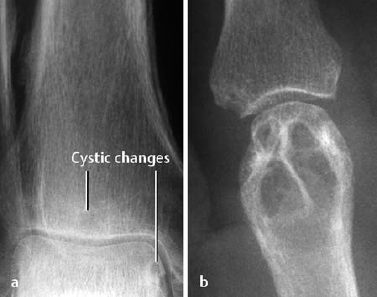
Joints | Radiology Key
CASE STUDY - a subchondral bone cyst in the stifle - Newmarket Equine Hospital - Newmarket Equine Hospital
![PDF] Percutaneous injection of bone cement (Cementoplasty) for the treatment of symptomatic subchondral cysts | Semantic Scholar PDF] Percutaneous injection of bone cement (Cementoplasty) for the treatment of symptomatic subchondral cysts | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/d05d22c0d7b1b2b785343c648a2a2c31e1d89fd2/3-Figure5-1.png)
PDF] Percutaneous injection of bone cement (Cementoplasty) for the treatment of symptomatic subchondral cysts | Semantic Scholar

OSTEOARTHRITIS - ACTIVE CARE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC

Subchondral cyst (geode) of the femoral head | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org

Cyst formation in the subchondral bone following cartilage repair - Gao - 2020 - Clinical and Translational Medicine - Wiley Online Library
![PDF] Arthroscopic Treatment of Subchondral Bony Cyst in Early Osteoarthritis of the Hip Joint Using Allogeneic Bone Graft: A Report of Two Cases | Semantic Scholar PDF] Arthroscopic Treatment of Subchondral Bony Cyst in Early Osteoarthritis of the Hip Joint Using Allogeneic Bone Graft: A Report of Two Cases | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/b87d6cdf4da375570ce7d412b52ae9cfb8edef4a/2-Figure1-1.png)
PDF] Arthroscopic Treatment of Subchondral Bony Cyst in Early Osteoarthritis of the Hip Joint Using Allogeneic Bone Graft: A Report of Two Cases | Semantic Scholar

Subchondral Bone Cyst: Causes, Treatment, and More

Subchondral Cyst Formation (Page 1) - Line.17QQ.com
/GettyImages-949352052-0d6d34cba31d4f3b827822698b68c0df.jpg)
Subchondral Sclerosis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment

Subchondral bone cysts complicated with bone remodeling turnovers in patients with knee osteoarthritis - Osteoarthritis and Cartilage

Subchondral Bone Cyst: Case 23 | SpringerLink
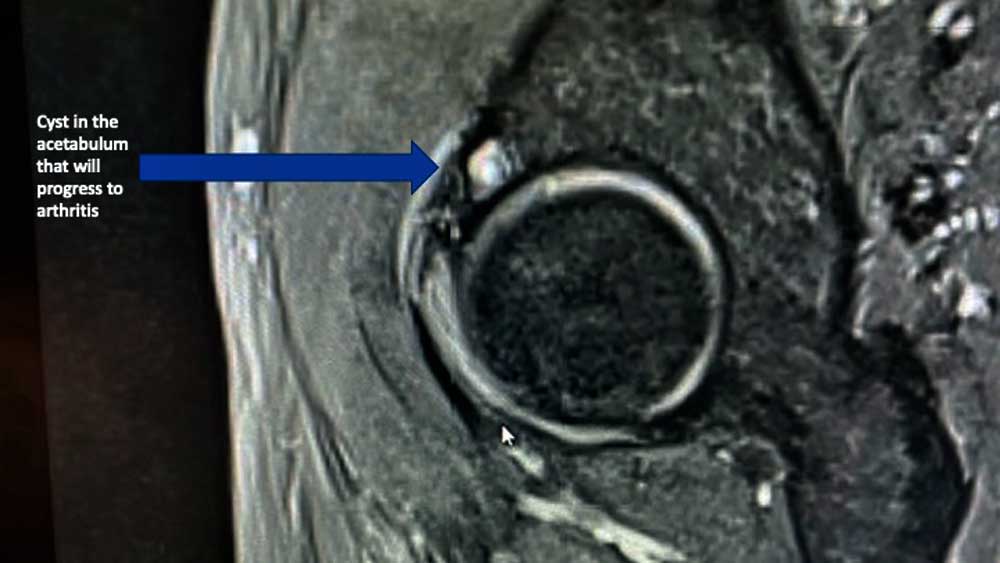
Hip Cysts | Acetabular Paralabral Cyst & Subchondral Cyst | FAI | Manhattan, New York City, NY
CARPOMETACARPAL SUBCHONDRAL CYSTS DUE TO REPETITIVE MOVEMENTS IN SHOEMAKER: A CASE REPORT

CC of Hip Joint (Black arrow) with large subchondral cyst (White arrow) | Download Scientific Diagram
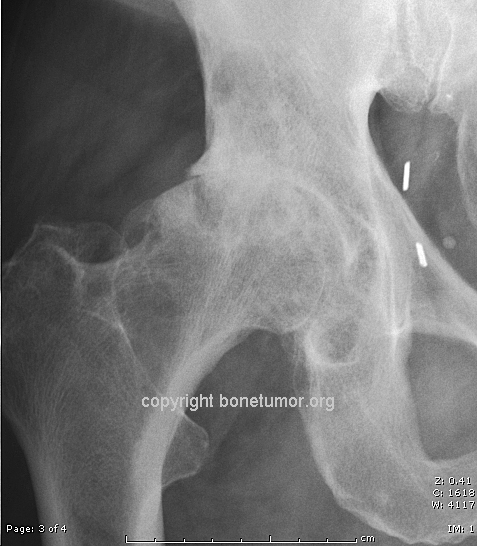
Subchondral cyst | BoneTumor.org
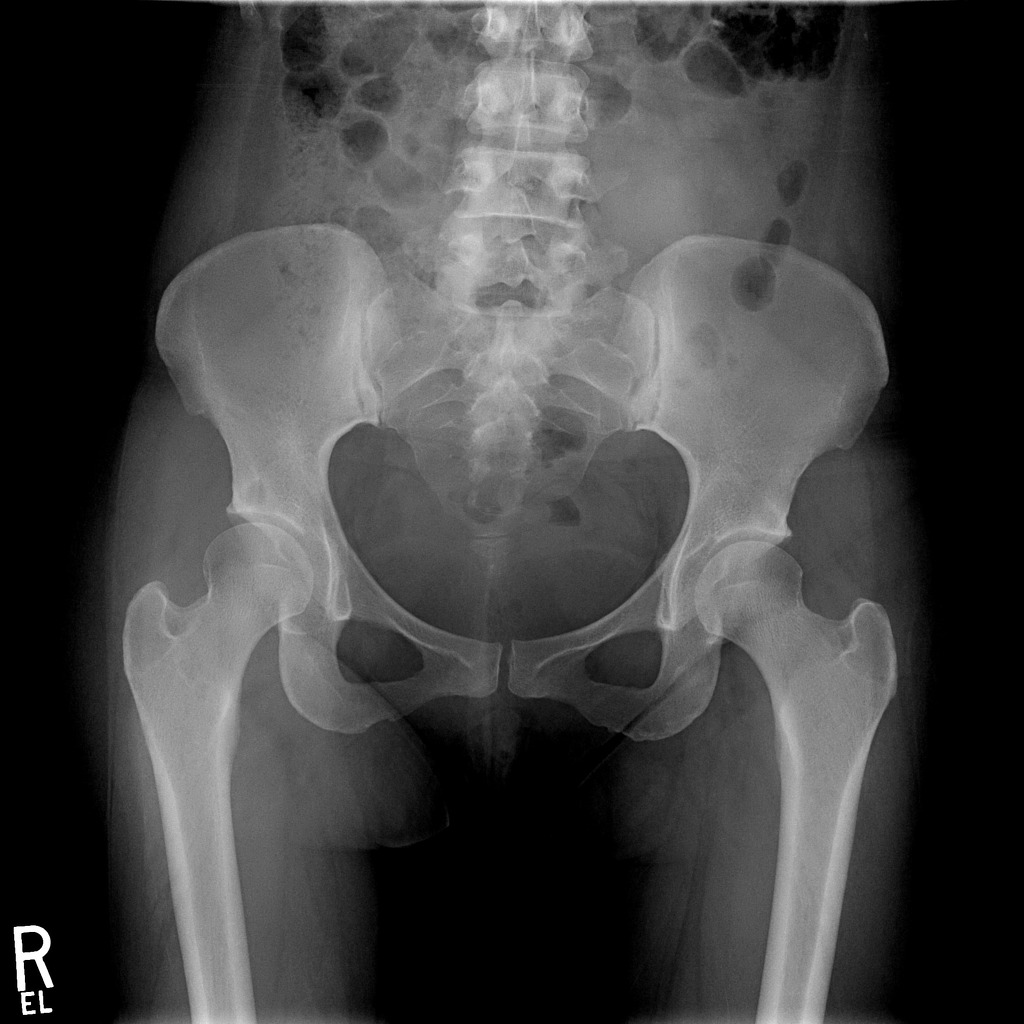
Primary cystic arthrosis of the hip | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org
![PDF] Arthroscopic Treatment of Subchondral Bony Cyst in Early Osteoarthritis of the Hip Joint Using Allogeneic Bone Graft: A Report of Two Cases | Semantic Scholar PDF] Arthroscopic Treatment of Subchondral Bony Cyst in Early Osteoarthritis of the Hip Joint Using Allogeneic Bone Graft: A Report of Two Cases | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/b87d6cdf4da375570ce7d412b52ae9cfb8edef4a/4-Figure3-1.png)
PDF] Arthroscopic Treatment of Subchondral Bony Cyst in Early Osteoarthritis of the Hip Joint Using Allogeneic Bone Graft: A Report of Two Cases | Semantic Scholar

Endoscopic Shelf Acetabuloplasty for Treating Acetabular Large Bone Cyst in Patient With Dysplasia - ScienceDirect
Subchondral Bone Cyst – North Texas Farm and Ranch

Bone Cyst: The Case of the Missing Bone - Expert how-to for English Riders

Osteoarthritis and intervertebral disc degeneration: Quite different, quite similar - Rustenburg - 2018 - JOR SPINE - Wiley Online Library
Posting Komentar untuk "what is a subchondral cyst"