Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome Diagnosis Criteria
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome diagnosis criteria. Ophthalmologists should be familiar with the spectrum of clinical. 1 New clinical laboratory and experimental insights gained since then were addressed at the Eleventh International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Sydney Australia in 2006. All four criteria except that only two organssystems involved.
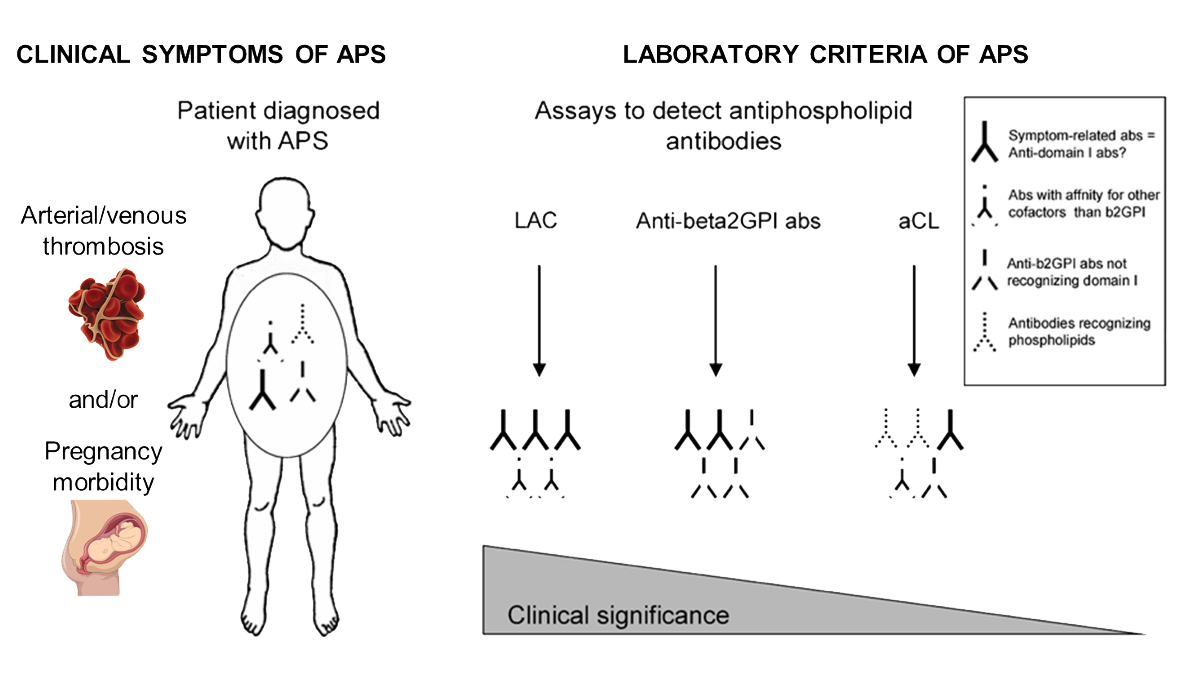
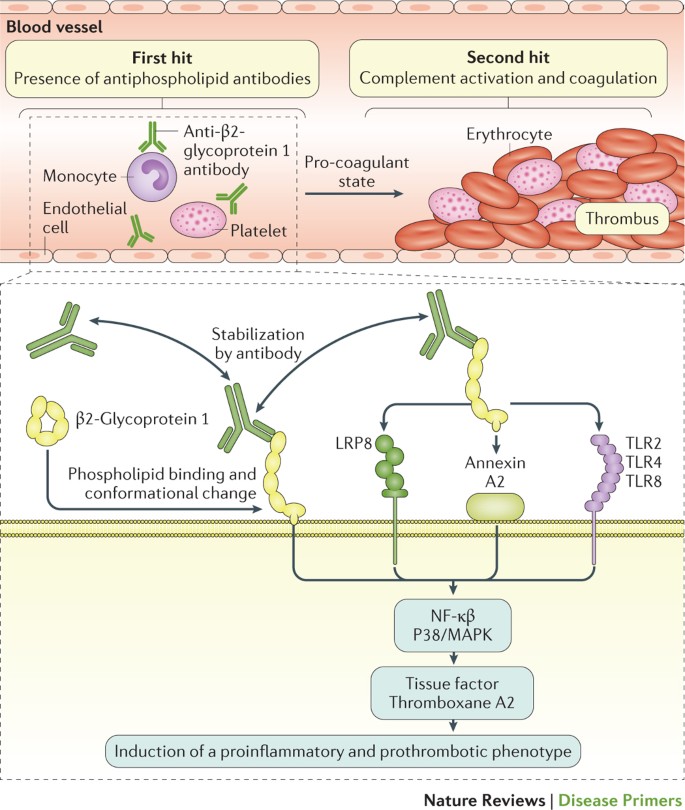
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome are available with increased sensitivity and specificity but lack of standardization and interassay and interlaboratory variation makes it difficult to determine their clinical value. The antiphospholipid syndrome APS 1 is an autoimmune disease defined by the presence of thromboembolic complications TEC andor pregnancy morbidity in the presence of persistently increased titers of antiphospholipid antibodies APAs. Antiphospholipid antibodies target β 2 -glycoprotein I.
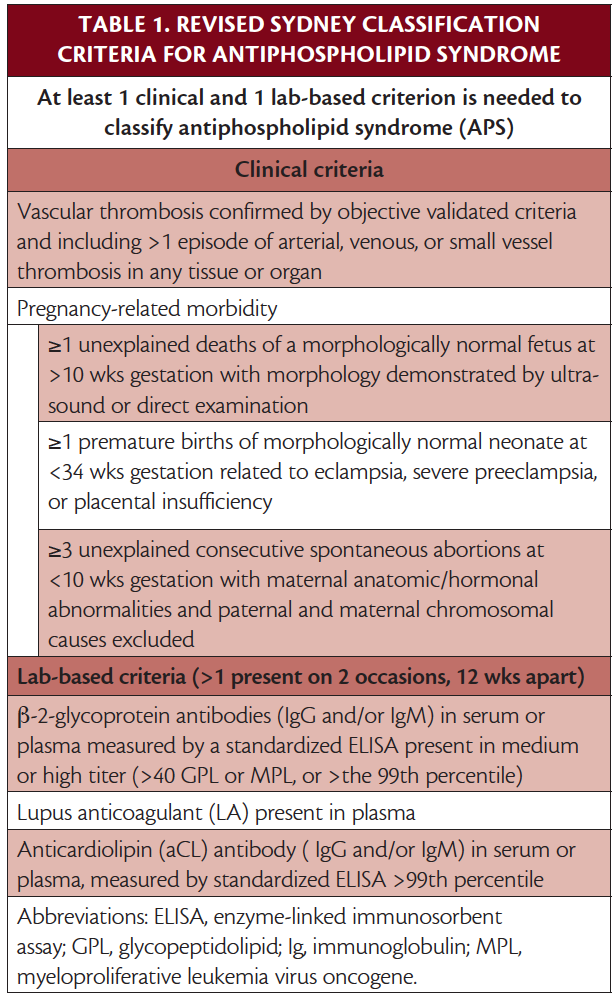
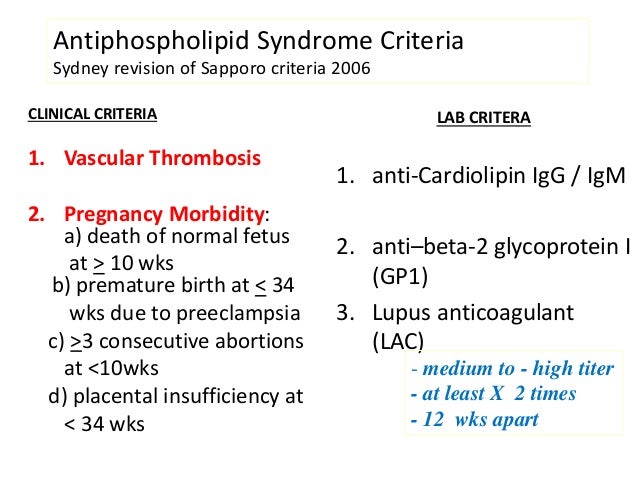
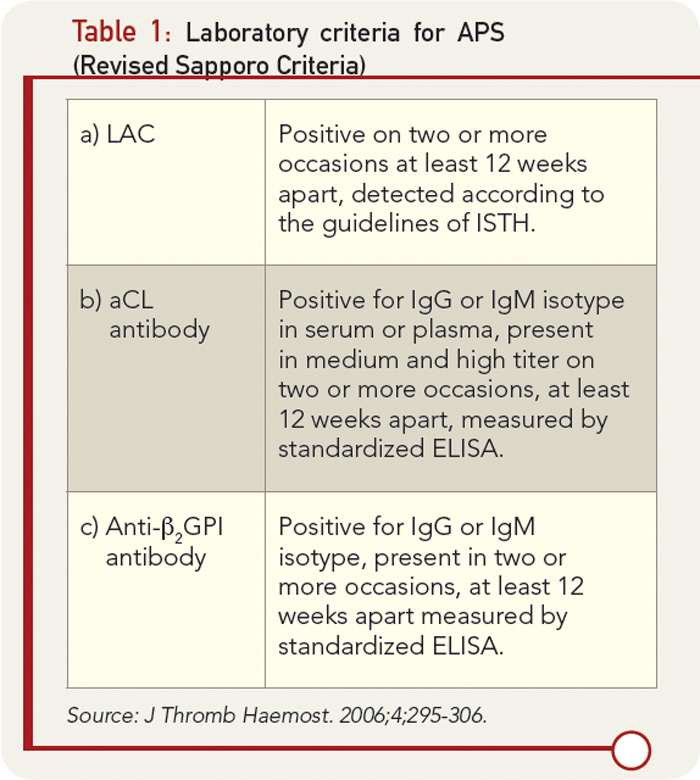
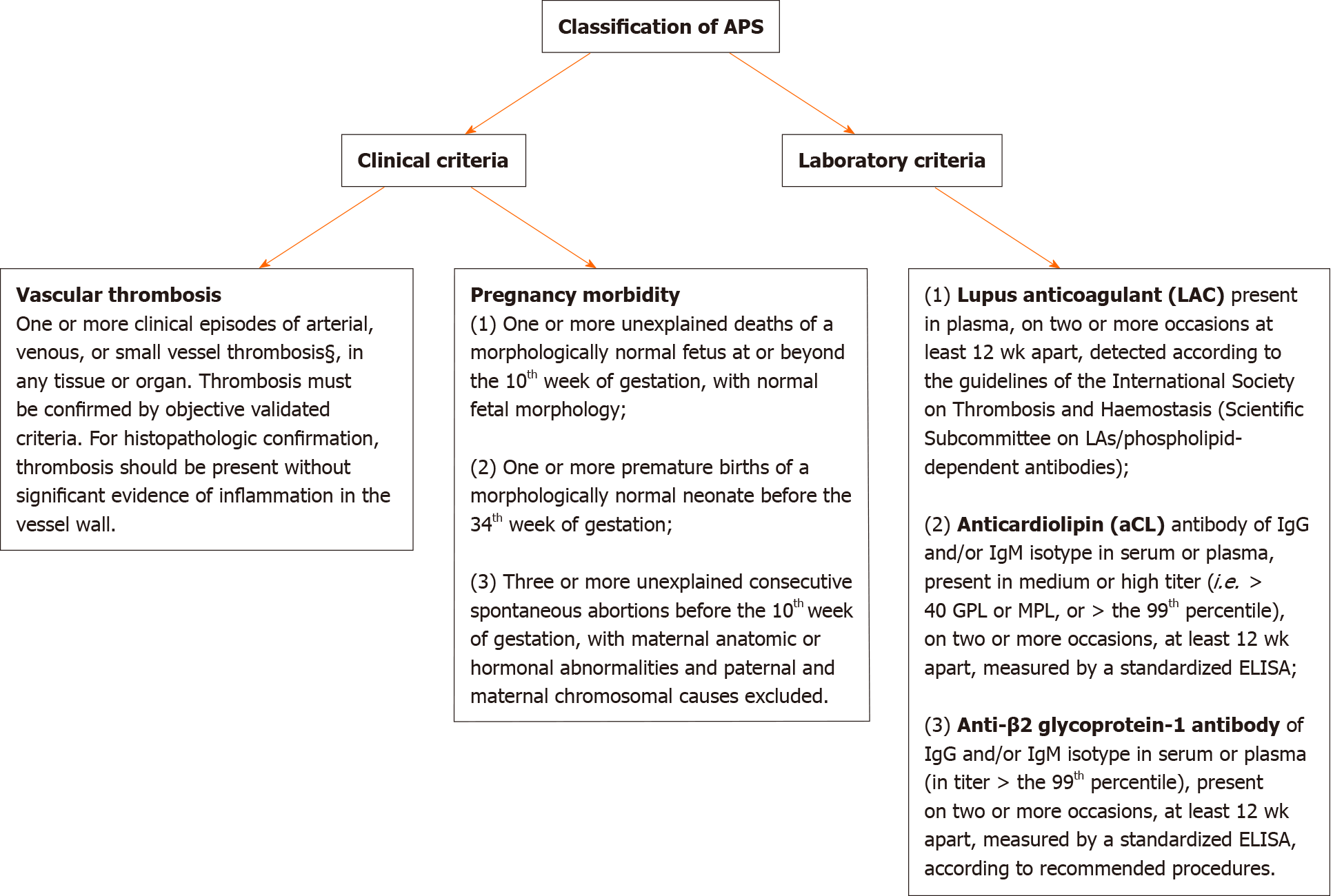
The original antiphospholipid syndrome APS classification criteria the Sapporo criteria published in 1999 helped galvanize research in this disorder. Medium to high levels of immunoglobulin G IgG or immunoglobulin M IgM anticardiolipin aCL Antibeta-2 glycoprotein I. Usually this is the result of an infection or a side effect of medication such as antibiotics.
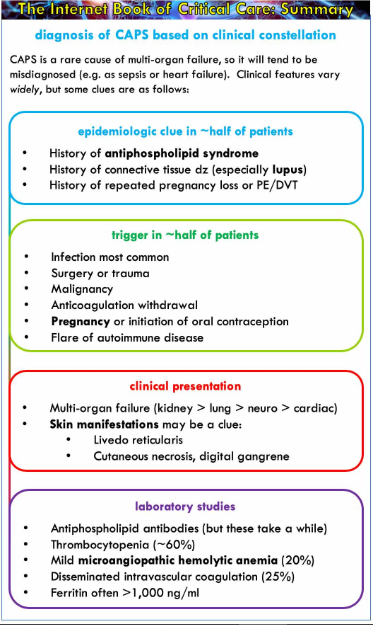
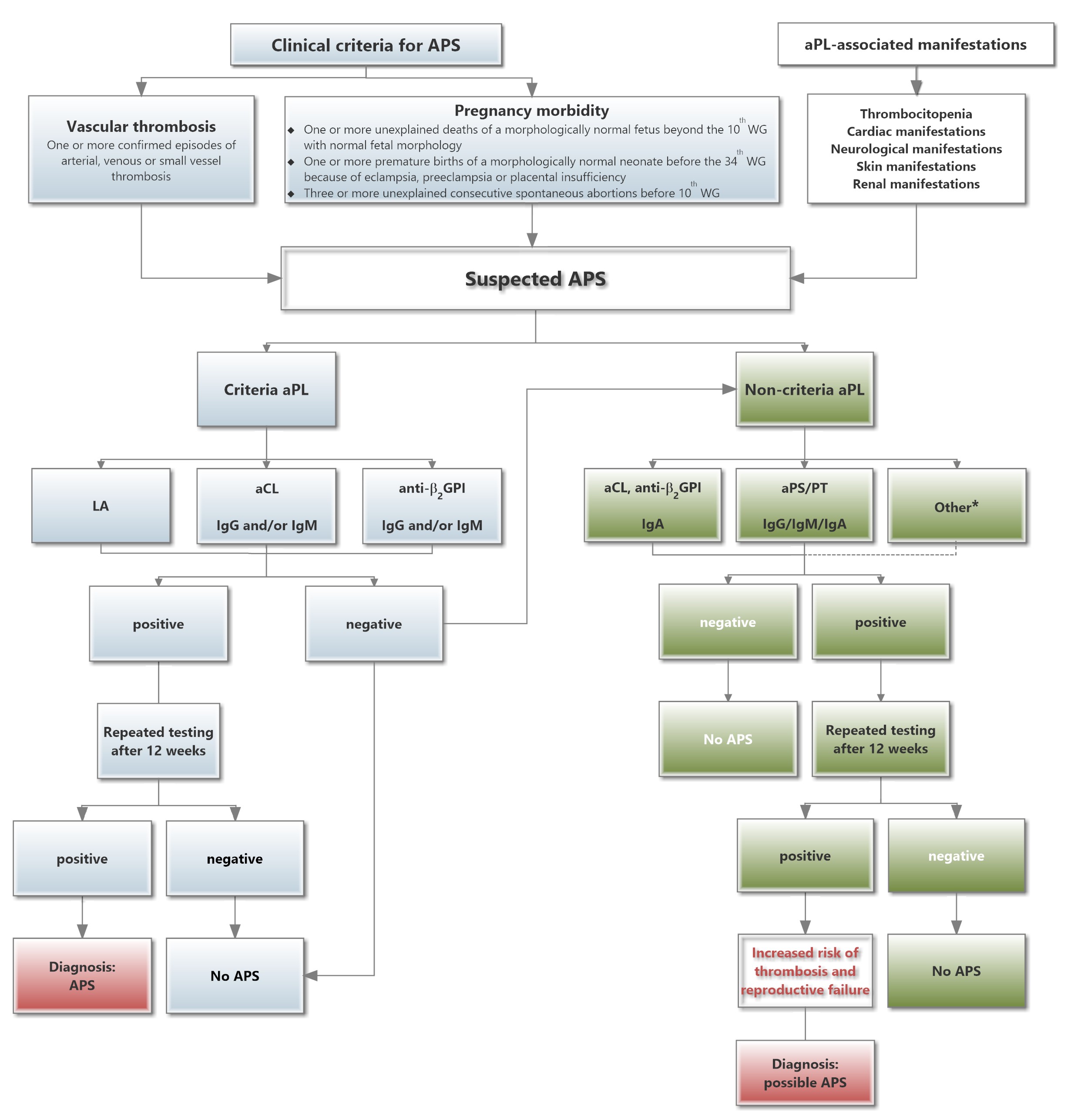
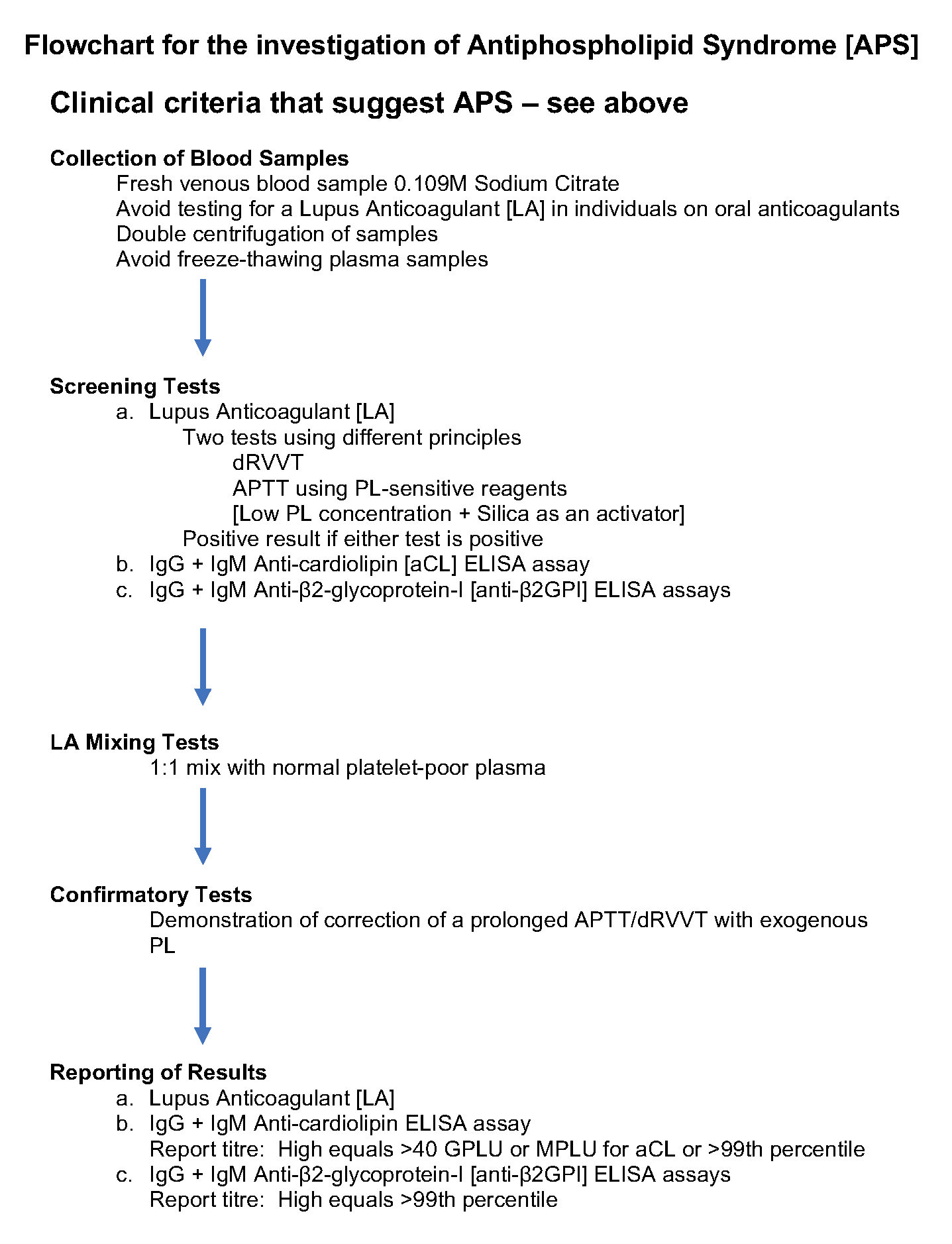
A strong index of suspicion must underlie investigation for antiphospholipid syndrome APS. Antiphospholipid syndrome APS is an autoimmune disorder defined by the presence of characteristic clinical features and specified levels of circulating antiphospholipid antibodies Box 1 and Box 2Diagnosis requires that at least one clinical and one laboratory criterion are met. 16 at least one clinical criterion vascular thrombosis or pregnancy morbidity and one laboratory criterion LAC.
Because approximately 70 of individuals with APS are female 1 it is reasonably prevalent among women. Antiphospholipid syndrome APS is characterized by venous or arterial thrombosis andor an adverse pregnancy outcome in the presence of persistent laboratory evidence of antiphospholipid antibodies aPL. APS is a systemic autoimmune disease defined by thrombotic or obstetrical events that occur in patients with persistent antiphospholipid antibodies.
A diagnosis of APS can only be made after 2 abnormal blood test results with at least a 12-week gap between them. Antiphospholipid syndrome can be primary or secondary. Criteria 1 2 and 4 everything except pathological confirmation.
Classification criteria for definite APS are met when at least one clinical criterion thrombosis or pregnancy morbidity and one laboratory criterion lupus anticoagulant LAC anticardiolipin antibodies aCL or beta2glycoprotein I antibodies aβ2GPI are present. Revised Sapporo Criteria for Antiphospholipid Syndrome APS 22 April 2019 Guillermo Firman Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome APS is an autoimmune disorder characterized by vascular thrombosis complications during pregnancy and the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies APL in plasma.
Because approximately 70 of individuals with APS are female 1 it is reasonably prevalent among women.
16 at least one clinical criterion vascular thrombosis or pregnancy morbidity and one laboratory criterion LAC. The diagnostic criteria require one clinical event ie. Antiphospholipid syndrome APS is characterized by venous or arterial thrombosis andor an adverse pregnancy outcome in the presence of persistent laboratory evidence of antiphospholipid antibodies aPL. Usually this is the result of an infection or a side effect of medication such as antibiotics. Criteria 1 2 and 4 everything except pathological confirmation. APS is a systemic autoimmune disease defined by thrombotic or obstetrical events that occur in patients with persistent antiphospholipid antibodies. Antiphospholipid syndrome can be primary or secondary. The original antiphospholipid syndrome APS classification criteria the Sapporo criteria published in 1999 helped galvanize research in this disorder. Abstract First described in the early 1980s antiphospholipid syndrome APS is a unique form of acquired autoimmune thrombophilia in which patients present with clinical features of recurrent thrombosis and pregnancy morbidity and persistently test positive for the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies aPL.
2 On the basis of these discussions amendments to the Sapporo. Revised Sapporo Criteria for Antiphospholipid Syndrome APS 22 April 2019 Guillermo Firman Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome APS is an autoimmune disorder characterized by vascular thrombosis complications during pregnancy and the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies APL in plasma. Ophthalmologists should be familiar with the spectrum of clinical. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome APS The diagnosis of APS requires at least 1 of the following clinical criteria and 1 of the following laboratory criteria. APS occurs either as a primary condition or in the setting of an underlying disease usually systemic lupus erythematosus SLE. The antiphospholipid syndrome APS 1 is an autoimmune disease defined by the presence of thromboembolic complications TEC andor pregnancy morbidity in the presence of persistently increased titers of antiphospholipid antibodies APAs. Laboratory criteria include any of the following see also Lab Studies.
























Posting Komentar untuk "Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome Diagnosis Criteria"