The Wnt Signaling Pathway In Development And Disease
The wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Considerations for Studying WNT4 in Development and Disease. The Wnt signaling pathway is an evolutionarily conserved highly complex signaling pathway that is critical for development differentiation and cellular homeostasis. The WNT signal transduction cascade controls myriad biological phenomena throughout development and adult life of all animals.
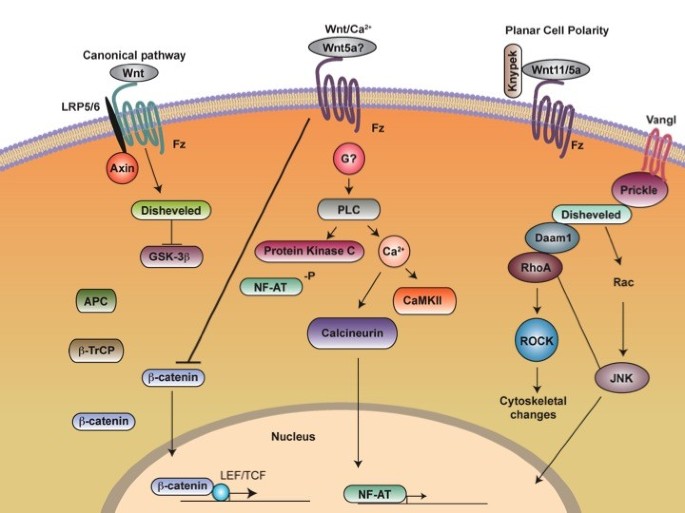
Written by a team of expert reviewers the book provides clear and concise coverage of the. The canonical Wnt signaling pathway. A critical mediator of key cell-cell signaling events during embryogenesis is the highly conserved Wnt family of secreted proteins.
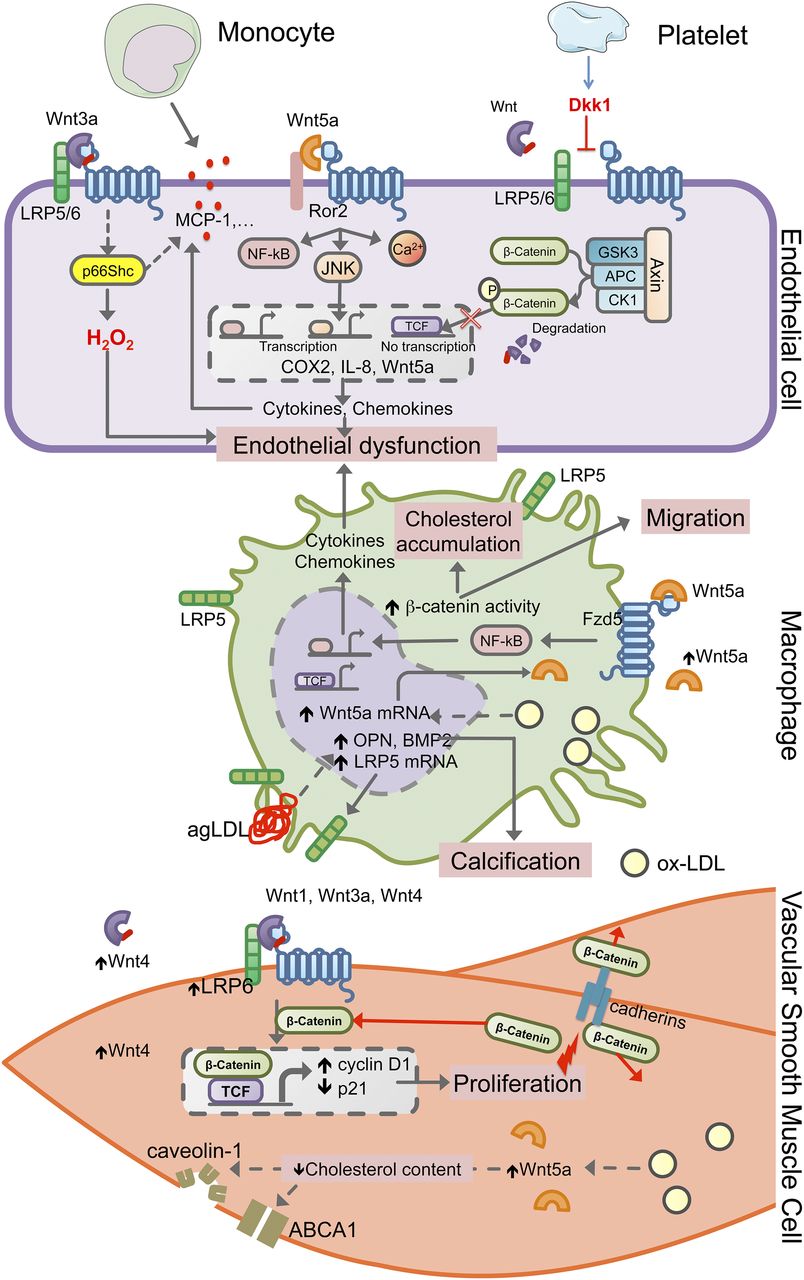
WNT4 dysregulation is associated with a spectrum of sex development and womens health issues that should be a major consideration in research when considering sex as a biological variable and in clinical studies that use inhibitors of Wnt signaling. Wnts are secreted glycoproteins that play essential roles in embryogenesis and cortical development. Wnt signaling is required for different aspects of cardiac and vascular development including myocardial specification cardiac morphogenesis and cardiac valve formation as well as endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation.
Wnts are evolutionarily conserved major regulatory factors in both development and disease. Wingless-related integration site Wnt signaling has proven to be a fundamental mechanism in cardiovascular development as well as disease. Crosstalks among Wnt signaling pathways and miRNAs are critical for cell differentiation.
In parallel aberrant Wnt signaling underlies a wide range of pathologies in humans. Components of Wnt pathways are regulated by microRNAs. Tight control of cell-cell communication is essential for the generation of a normally patterned embryo.
The Wnt signaling pathway is one of the central morphogenic signaling pathways regulating early vertebrate. Wnt-β-catenin signalling tightly controls embryogenesis including hepatobiliary development maturation and zonation. Defective Wnt signaling can result in different cardiac and vascular abnormalities.
Therefore the primary purpose of our study is to understand the expression of Wnt pathway-related genes in the early utricle. Wnt signaling in development and disease Abstract.
Wntβ-catenin signaling and disease.
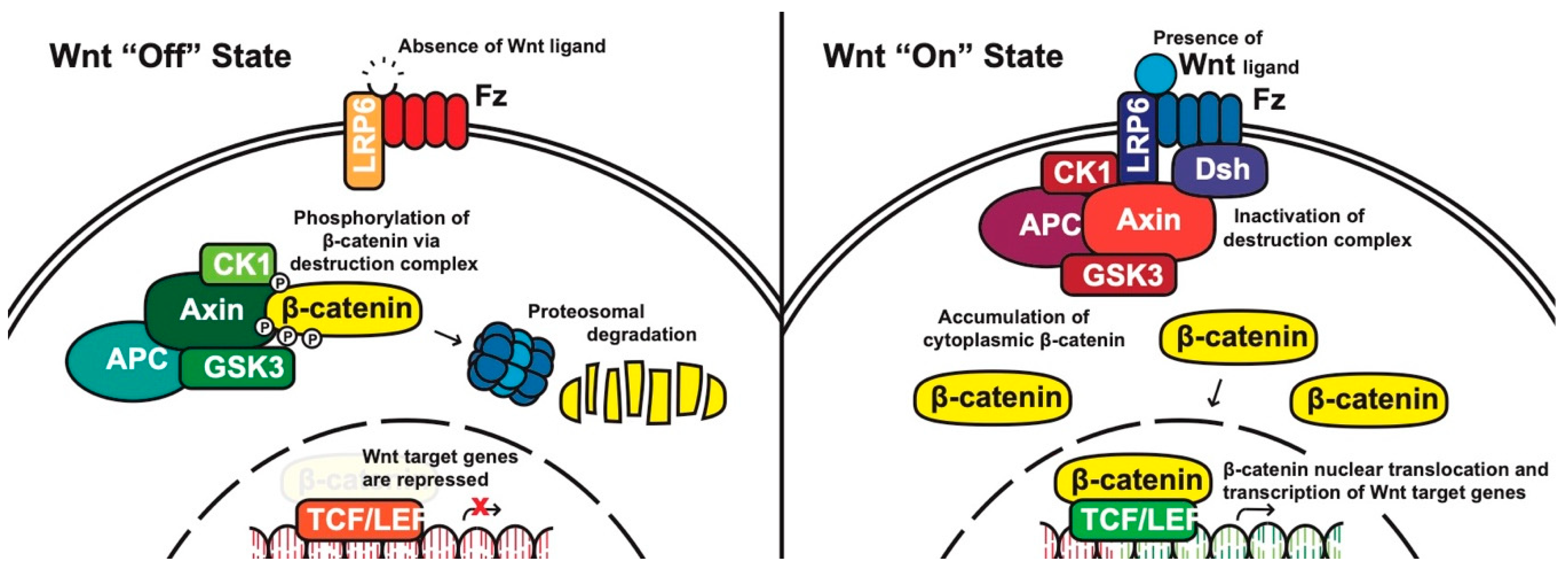
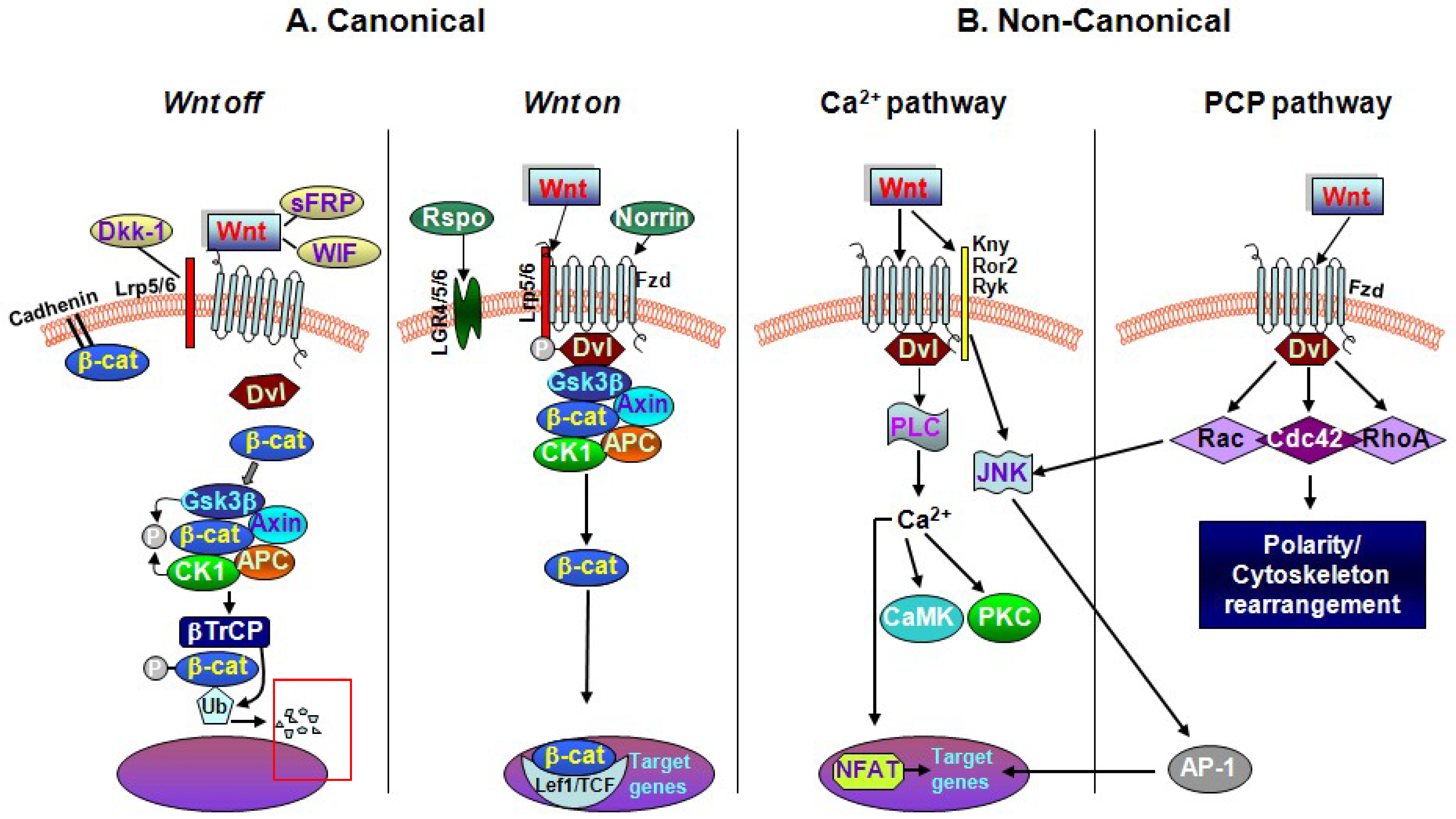
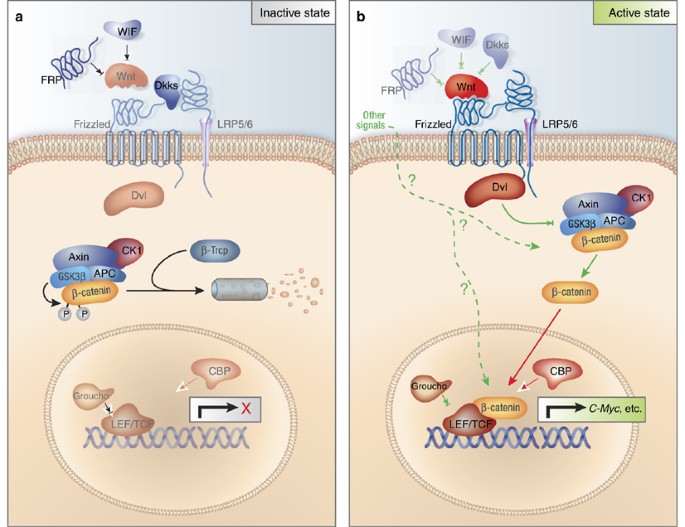
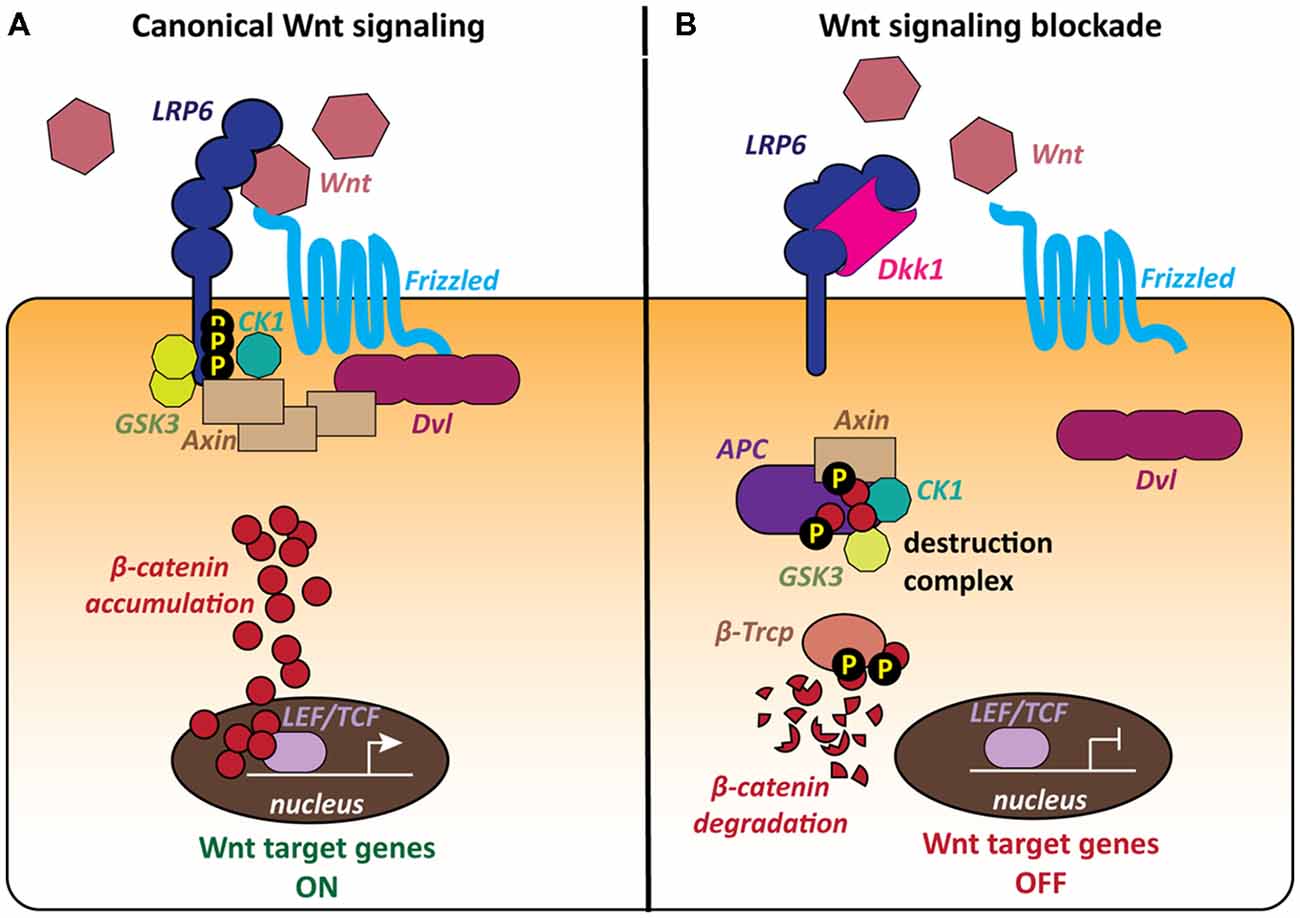
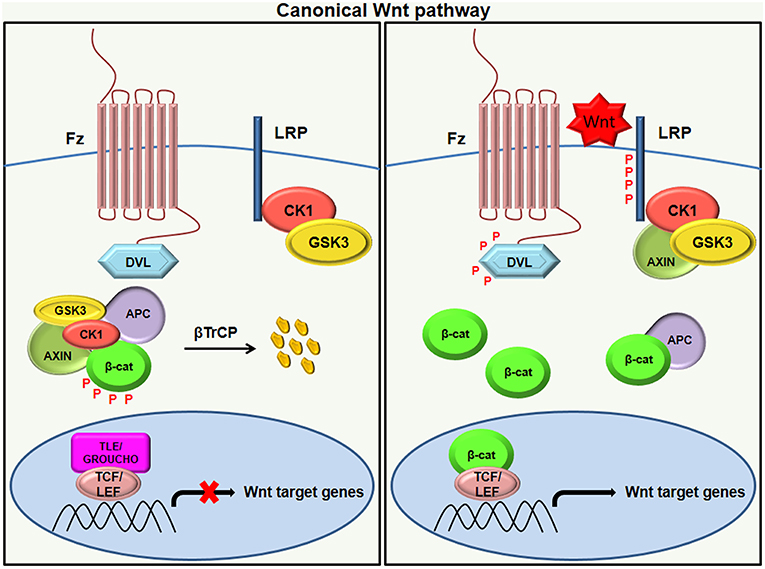
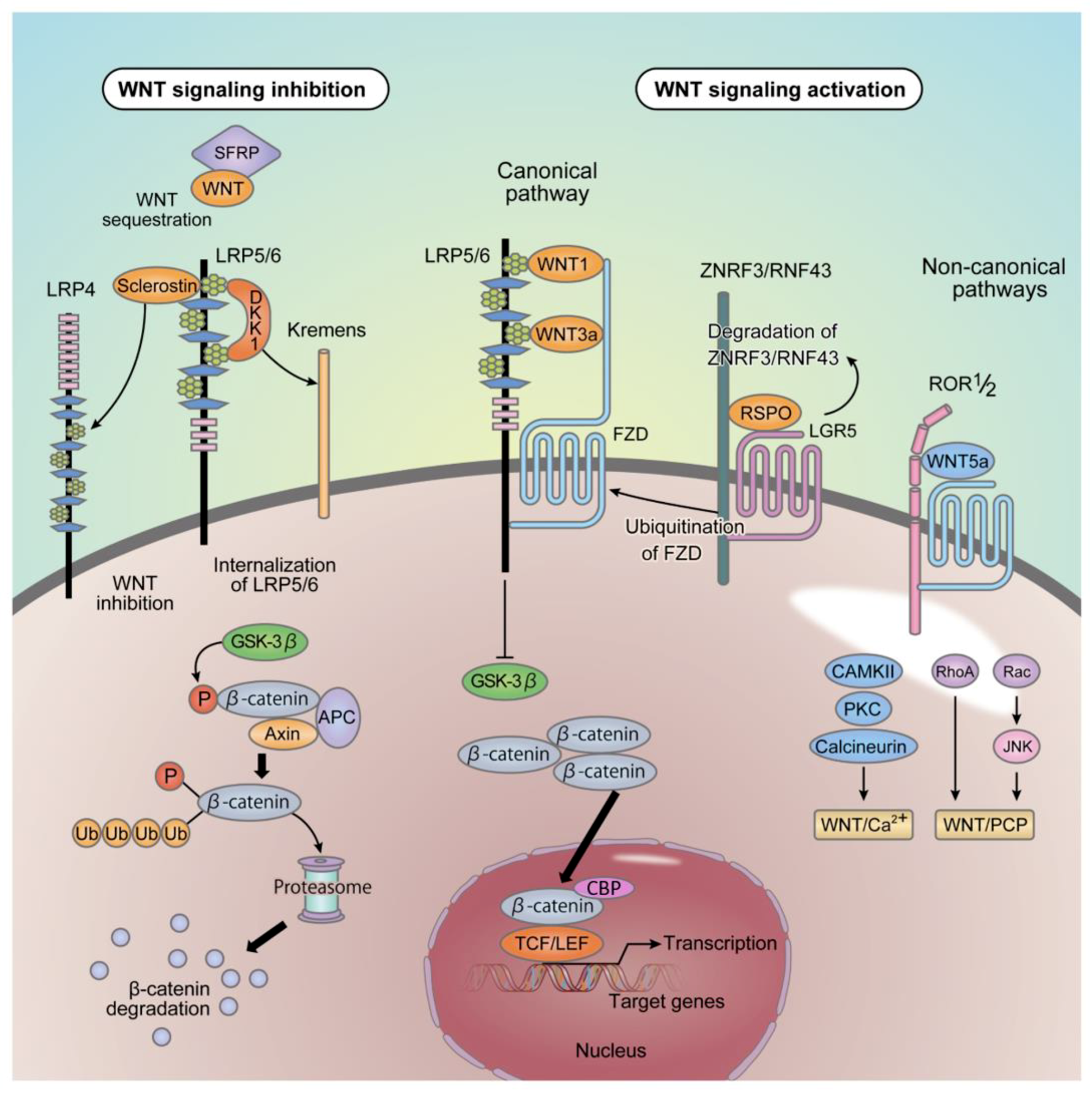
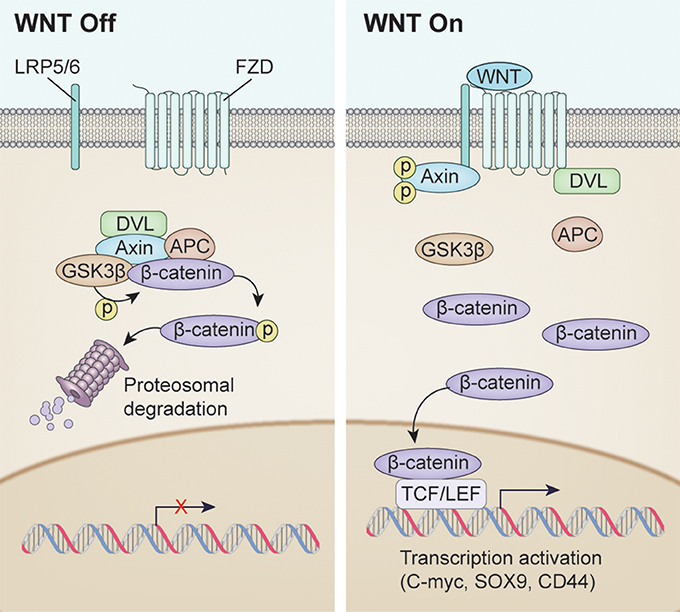
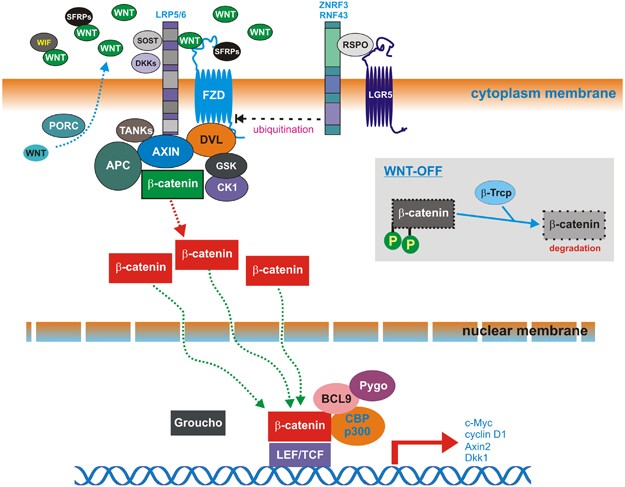
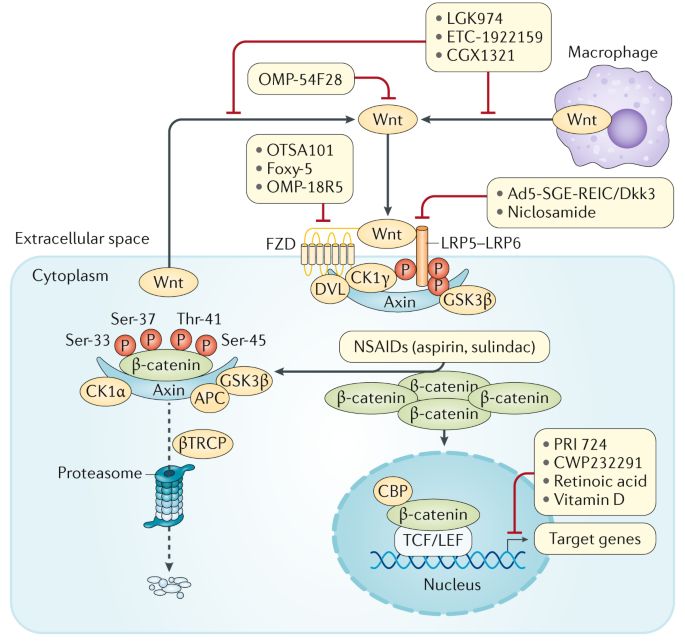
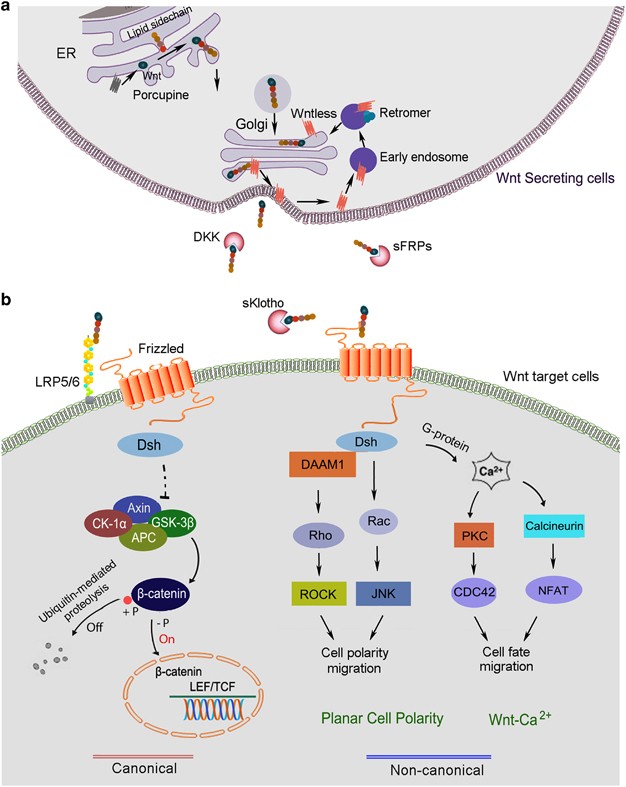
Wnt signaling is involved in virtually every aspect of embryonic development and also controls homeostatic self-renewal in a number of adult tissues. Considerations for Studying WNT4 in Development and Disease. The canonical Wnt-β-catenin pathway is a complex evolutionarily conserved signalling mechanism that regulates fundamental physiological and pathological processes. In cells not exposed to a Wnt signal left panel β-catenin is degraded through interactions with Axin APC and the protein kinase GSK-3. Wingless-related integration site Wnt signaling has proven to be a fundamental mechanism in cardiovascular development as well as disease. The WNT signal transduction cascade controls myriad biological phenomena throughout development and adult life of all animals. Wnt signaling in Development and Disease. Components of Wnt pathways are regulated by microRNAs. Germline mutations in the Wnt pathway cause several hereditary diseases and somatic mutations are associated with cancer of the intestine and a variety of other tissues.
Wnt signaling is required in most embryonic developmental processes in both invertebrates and vertebrates. The canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Wnt-β-catenin signalling tightly controls embryogenesis including hepatobiliary development maturation and zonation. About this book. The canonical Wnt-β-catenin pathway is a complex evolutionarily conserved signalling mechanism that regulates fundamental physiological and pathological processes. Tight control of cell-cell communication is essential for the generation of a normally patterned embryo. Wnt signal cascade is an evolutionarily conserved developmental pathway that regulates embryogenesis injury repair and pathogenesis of human diseases.
























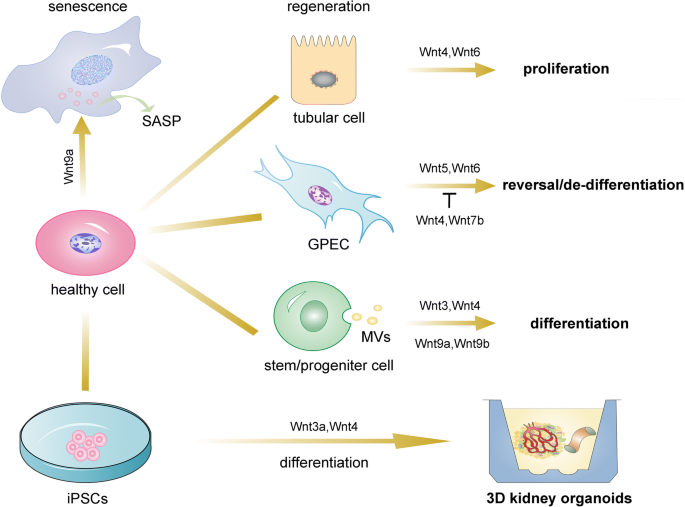



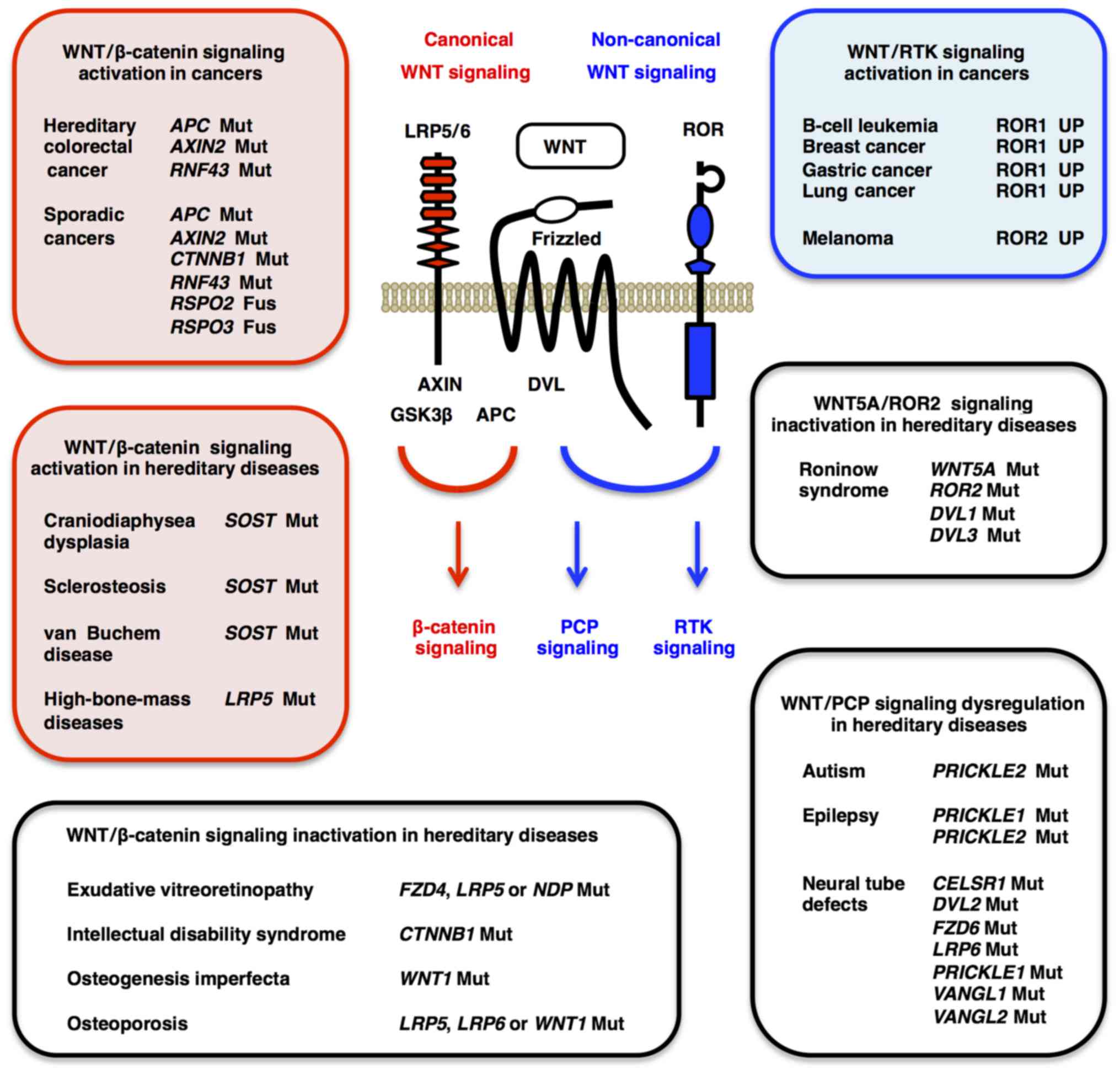

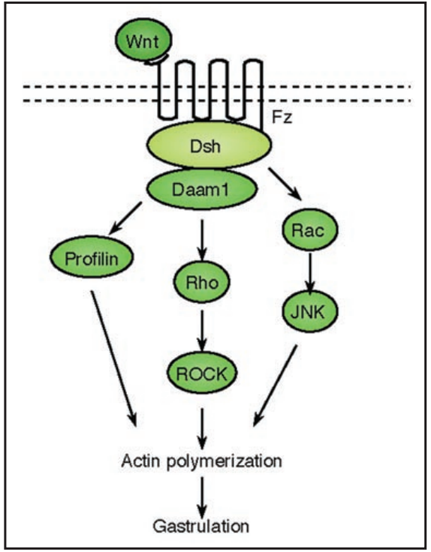
Posting Komentar untuk "The Wnt Signaling Pathway In Development And Disease"